Since the Apollo era, the moon has remained a symbol of untapped potential and a gateway to new frontiers. Recent developments in space exploration, driven by both governmental and private initiatives, a combination of scientific curiosity, and the pursuit of potential economic opportunities, have reignited the passion for lunar missions once again. The prospect of returning to the moon, not as a mere visit but as a sustainable economic endeavor, has sparked a wave of innovative ideas and bold aspirations leading to a so-called Moon rush. So let’s look deeper into the topic.
Evolution of the Lunar Economy Since the Apollo Era
“Right now, the Moon is the target of more missions than at any time since the Apollo era – over the next 10 years, 400 missions are projected,” said Jim Free, the associate administrator for the Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington, D.C.
The Apollo missions of the late 1960s and early 1970s represented the first and only time that humans have set foot on the lunar surface. However, as the result of the Apollo program, the focus of space exploration was shifted to low Earth orbit and beyond.
The concept of a lunar economy, centered around the utilization of lunar resources for scientific, commercial, and exploratory purposes, began to gain traction only in the early 21st century. This shift in focus was driven by a growing recognition of the Moon’s potential as a platform for supporting future space missions, including those aimed at Mars and beyond. Additionally, advancements in robotics, additive manufacturing, and in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) technologies have bolstered the prospects of establishing a sustained human presence on the Moon.
NASA’s Plans and Involvement in the Lunar Economy
“Building the foundations of a lunar economy for returning to the Moon are really rooted in what NASA has always done,” said Jim Free in his interview with FT.
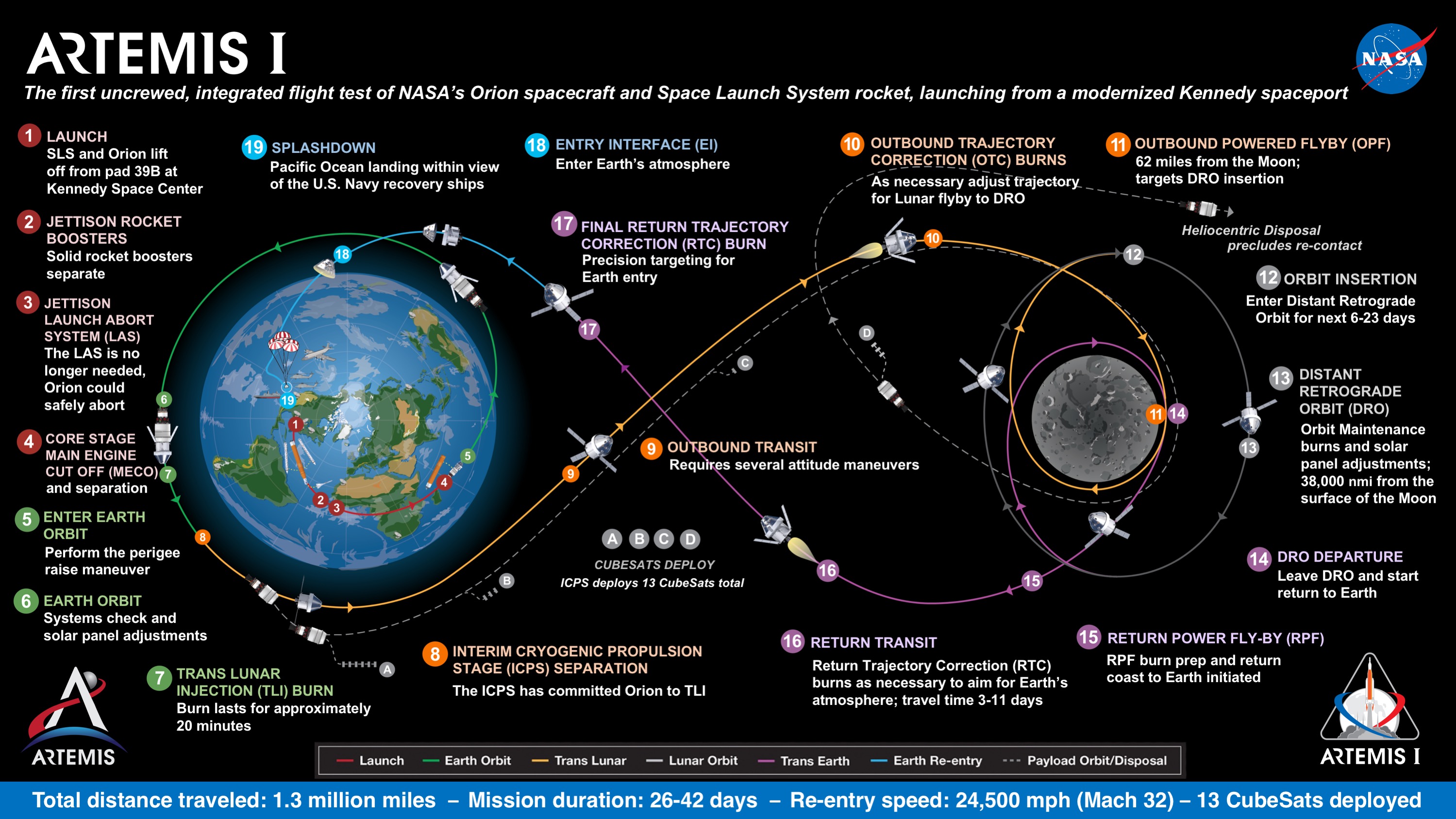
As a key player in space exploration and scientific research, NASA plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of the lunar economy. In recent years, NASA has outlined ambitious plans for returning humans to the Moon under the Artemis program, which aims to establish a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface by the end of the decade. Central to NASA’s vision for the Artemis program is the Lunar Gateway, a space station that will orbit the Moon and serve as a staging point for lunar missions, as well as a hub for scientific research and international collaboration.
However NASA’s involvement in the lunar economy extends beyond the Artemis program, encompassing a broad range of initiatives aimed at unlocking the potential of lunar resources and advancing the frontiers of space exploration, as they said that they see the Moon adaptation as a training ground for living and working on Mars.
Additionally, NASA is turning to the private sector to help cut the cost of its mission. Instead of concentrating on building a rocket, it wants to buy a ride from companies such as SpaceX and Blue Origin. This is one of the fundamental differences from the Apollo era. It means that others could use those services, too. Therefore, NASA’s collaboration with international partners, commercial entities, and academic institutions underscores the agency’s commitment to fostering a vibrant lunar economy that transcends national boundaries and harnesses the collective expertise and resources of the global space community.
Viability of the Lunar Economy and Potential Challenges

The prospect of establishing a sustainable lunar economy holds immense promise for advancing the frontiers of space exploration and resource utilization. However, it is essential to critically examine its viability and consider the potential challenges that may impede its realization.
Several factors contribute to the potential success of the lunar economy, including the abundance of lunar resources, the strategic significance of the Moon as a platform for deep space exploration, and the advancements in technology that enable the utilization of lunar resources for scientific, commercial, and exploratory purposes. Additionally, a significant role in the lunar economy’s viability plays the presence of water ice and other volatiles in permanently shadowed regions of the Moon, which can be extracted and utilized for supporting human missions, generating propellant, and sustaining life on the lunar surface. The availability of these resources holds significant implications for reducing the cost and complexity of deep space missions, as well as enabling the establishment of a sustained human presence on the Moon.
While the prospects of the lunar economy are promising, several challenges must be addressed to realize its full potential. These challenges include the technical, logistical, and economic complexities inherent in establishing and maintaining a robust lunar infrastructure, as well as the imperative of addressing environmental and ethical considerations associated with lunar resource utilization.
Conclusion: personal opinion, the Promise of a Sustainable Lunar Economy
As we stand on the threshold of a new era in space exploration, the promise of a sustainable lunar economy beckons with boundless potential and transformative opportunities. The resurgence of interest in lunar missions, fueled by the vision of returning to the moon not as a mere destination but as a sustainable platform for scientific discovery, resource utilization, and human habitation, heralds a paradigm shift in our relationship with the cosmos.
The viability of the lunar economy, while accompanied by formidable challenges, in my opinion, still holds a great chance of success, as all of those challenges could be solved, and the factors of success definitely outweigh them. However I hold a sceptical opinion on the idea of whether it will really happen in the near future, as we always heard about companies’ ambitious goals connected with the space and lunar exploration and most often it were just the words only; So whether it will really come into action is still under a question. Thus, the pursuit of a sustainable lunar economy is not merely a scientific or economic endeavor; it is a testament to our enduring spirit of exploration, our capacity for ingenuity, and our responsibility to chart a course toward a future that extends beyond the boundaries of our capabilities. So, let’s wait and see what the new Moon rush will bring to us.
What is your opinion on the new lunar economy? Do you think it may really come to life?
Sources(reference):
- https://www.economist.com/briefing/2023/09/27/how-microsoft-could-supplant-apple-as-the-worlds-most-valuable-firm (the news were the idea was taken from)
- https://www.economist.com/science-and-technology/2023/08/16/a-pair-of-indian-and-russian-probes-approach-the-moon (the news which also gave the reason to write about Moon rush)
- https://www.nasa.gov/specials/artemis/ (NASA’s Artemis project for exploration of the lunar surface, connected with the idea of lunar economy)
- https://www.nasa.gov/humans-in-space/growing-the-lunar-economy/ (NASA’s article on growing lunar economy and how it will look like)
- https://youtu.be/B2-8wrF9Okc?si=PgiOqOw7e-Im9txl (Microsoft’s own video presentation of the product) (video about NASA’s collaboration with SpaceX which was mentioned)
AI generators used:
- ChatSonic (key words: lunar economy, new moon rush, success and failure, NASA)
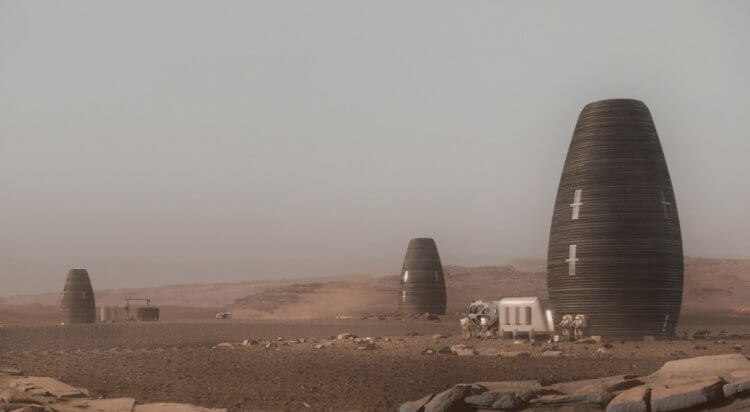


 Back in 2018, NASA researchers realized that some structures could be built from mushrooms. First, people build a primitive frame and then grow a special type of mushrooms under it, which wraps around the structure and takes its shape. When the structure takes its final form, the mushrooms can be heat treated and made clean and dry. In the picture, you can see that things made of mushrooms look disgusting and scary. Scientists want to make “mushroom houses” out of 3 layers. The first is mushrooms, the second is out of bacteria and the last one is ice. But they didn’t mention where to take so much water on Mars and how to prevent ice from melting.
Back in 2018, NASA researchers realized that some structures could be built from mushrooms. First, people build a primitive frame and then grow a special type of mushrooms under it, which wraps around the structure and takes its shape. When the structure takes its final form, the mushrooms can be heat treated and made clean and dry. In the picture, you can see that things made of mushrooms look disgusting and scary. Scientists want to make “mushroom houses” out of 3 layers. The first is mushrooms, the second is out of bacteria and the last one is ice. But they didn’t mention where to take so much water on Mars and how to prevent ice from melting.