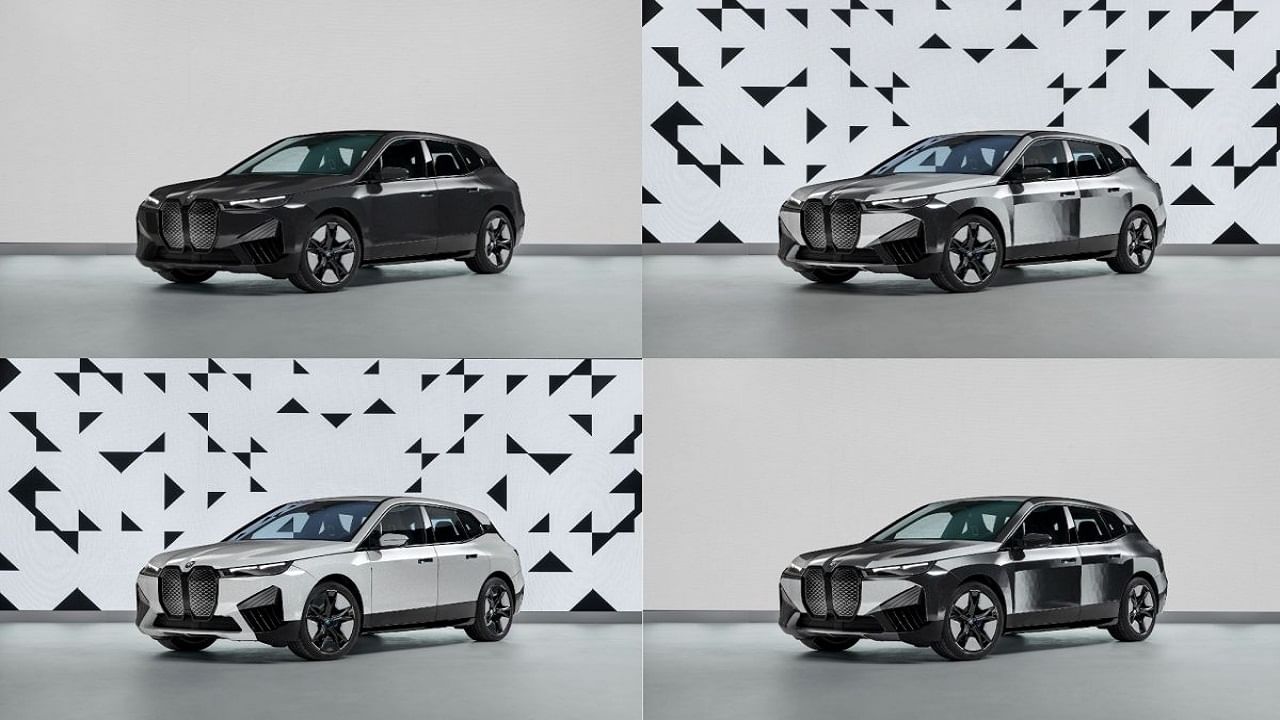
Electrophoretic technology was used to enable the color change function of the BMW IX Flow. – this car dresses and expresses the mood of the driver or its passengers. That is why we tried to create the appropriate technology to enable new experiences – said Christopher Grote, vice president of the bavarian company responsible for electronic solutions during the press conference. Changing the color is also possible while driving, e.g. when we are driving in hot weather and the black color becomes hotter. Then we press the appropriate button, pop… and we change che color of our car to white. In the implementation of this project, BMW cooperated with E-link, which has Sony and Amazon among its customers, and the technology was previously used in Kindle readers. The BMW E-link application works thanks to a special foil containing colored pigments, which covers the entire car. Through stimulation with electrical stimuli, the pigments float to the surface, and as a result, its color changes. “the challenge is not so much the technology as applying to the car”, admitted Christopher Grote.
Adrian van Hooydonk, head designer of the brand and head of BMW Group design makes no secret that the color change technology in the IX Flow concept is only part of BMW’s plan to develop products that stimulate all the senses and are “human oriented”. BMW intends to spend over 30 billion euro on these innovations by 2025. “For us, digitization is the total experience and emotion it can create”, said van Hooydonk. BMW was going to show the IX Flow at the Consumer Electronics Show (CES) taking place in Las Vegas. The company planned a full program there with the participation of partners and media, but eventually abandoned this presentation in favor of an online premiere in Munich. The reason was the increase in the incidence of coronavirus.
The ability to change the color of the car, also while driving, is a technological novelty, but not a revolution. There has been a reflective chameleon varnish on the market from some time. A car painted with it may have different shades depending on how the light shines on the surface of the car. There are also paints that change color under the influence of heat, and soon in Audi cars it will be possible to do this with the use of an on-board computer at any time. Adaptive color change can contribute to additional environmental benefits. According to Audi, cars with black lacquer consume 1-2 percent more energy in the summer, so more energy is needed to cool down the hot air. In its “colorful” strategy, Audi plans to use special foils applied to the base coat. Modifying the displayed shades results in a different color. However, it will not be a change as drastic as in the BMW IX Float, because the color will change, for example, from light blue to darker blue.
Kozminski Techblog
A blog on technology, run by Kozminski University students and supervised by NeRDS
Monthly Archives: June 2022
What are NFTs?
So an NFT is not the artwork itself, but a kind of digital certificate or signature. You can think of the NFT as a unique notation of who owns a particular thing. This thing can be, for example, a small pixel image like the now famous Cryptopunks, but also the very first Twitter tweet or digital music. The NFT serves as a certificate that states: person X is currently the owner of file Y, which is located at Internet address Z.
The abbreviation NFT stands for a non-fungible token. Without foreign words: a non-exchangeable token. A token is an asset, in simpler terms, a token. A counterexample to the NFT, i.e. a fungible, exchangeable token, would be a ten-euro bill. You can exchange this banknote at will for other ten-euro bills. The value and function of the banknote remain identical. (The serial number of the banknote is different – but that doesn’t matter for the purpose). A bitcoin or a beer token at the funfair would also be fungible tokens.
Now, what makes such a token non-exchangeable is that it is part of a blockchain. All transactions are publicly recorded in such a digital register. The blockchain is also distributed decentrally in different locations and represents a sophisticated accounting system. It is therefore not possible to transfer an NFT to someone else without authorization, without this transaction being visibly stored in the blockchain. The provenance history is therefore always clear – unlike with analog artworks, where provenance is often a problem. At the same time, the NFT records to which object it refers. Therefore, an NFT that refers to the picture of a cryptopunk is something different than an NFT that refers to the album of a music group.
Multiple NFTs can belong to one object. This may be by design when the NFTs are created. One use case would be “limited editions” of artwork, perhaps 1,000 copies of a graphic or piece of music. It is also conceivable that an NFT refers to a part of an object, for example, a tenth of a painting or a third of a piece of real estate. One problem: NFTs can also be created for an object without permission. The NFT Thefts initiative calls plagiarism, or pirated art, a growing problem in the NFT space.
Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake
You may have heard two similar terms in the cryptocurrency world: proof-of-work and proof-of-stake. These terms are used to distinguish whether a cryptocurrency is mined or not. However, sometimes the distinction between these terms can be confusing. Let’s take a look at what the difference between these terms is.
Let’s start with the simplest part – the proof-of-work (PoW) algorithm. This algorithm requires people to use computer hardware to process transactions. This hardware, also known as mining, uses its computing power to solve mathematical problems and is rewarded with a cryptocurrency. Bitcoin, and now Ethereum, still run on this algorithm. It was the first generation of blockchain, used in Bitcoin as the first cryptocurrency to use it.
The goal of proof-of-stake (PoS) is to achieve the same result as PoW – secure verification of transactions on the blockchain, but in this case, verifiers do so by providing a certain number of cryptocurrency tokens to a so-called staker, where they lock up their cryptocurrency and get a chance to verify the transaction, thereby receiving the associated reward and ensuring the security of the network. PoS is the next generation of how blockchain can work. It has several advantages over proof-of-work, such as you don’t need a super-powerful computer to verify transactions.

Automated battery and payload swaps for drones
Drones have been a growing trend from a simple gadget and a cool toy, to a whole industry that has many applications in every sector. However, one thing was always constraining drones, battery and payload management, that had to be managed by humans. It’s a process that is currently manually done by humans that have to swap batteries and payload by hand costing companies a lot of money to employ them and is far less effective than it could be.
However, Airrow, an LA startup has emerged with its take on it. IT works in a similar way to a 3D printer, in that it has the X, Y and Z axis on which it operates to swap the batteries for charged ones and put the out-of-juice battery to charge.
The system is in a very early stage, and the same goes for the company. However, the solution seems to be working for batteries, and the company says they are ready to develop a similar process for payloads.
The solution was shown during this year’s Amazon re:Mars conference and gathered a lot of interest. The company says the system will cost around $80’000-$100’000, which is not cheap. Though the bundle also includes a drone that would work in a closely knitted fashion with the autonomous changing station.
Unfortunately, the conference happened only a few days ago, and the company is so new, that there are no publications on how this system operates exactly (ideally with videos) available on the internet. Once I spot something, I will update this post with videos and photos. For now, I gathered these from the firm’s LinkedIn:



Reference:
https://www.linkedin.com/company/airrow/posts/?feedView=all
Airrow is automating battery and payload swapping for drones
3D scanning
How does 3D scanning work?
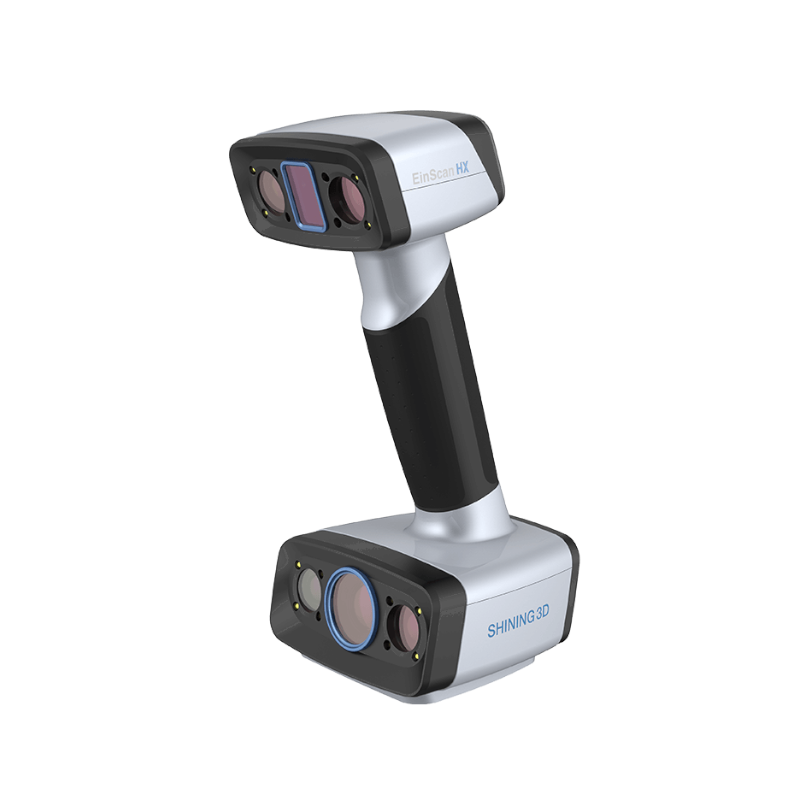

3D scanners, or to be precise Optical Measuring Machines are touchless metrologic systems made to catch data about a geometry of a given object – even those that are most complicated. During the process of 3D scanning, or in other words 3D digitalization, they change real objects into a shape of a precise and sophisticated digital model, in most cases saved as a network of STL triangles, which could easily be put under the process of quality control or reverse engineering.
Optical measuring machines stand out with a very good versatility and agilit. With these undoubtable benefits, there is no lack of quality in terms of measurement, where accuracy is more or less than 0.02mm.
A good example of such a machine is SCANTECH Simscan, which being on 20 cm long and weighs 0,5kg.
Types of 3D scanners
Each scanner is built out of a projection unit and set of cameras that are angled in a known process of calibration. This is necessary to generate a trustworthy data that are describing the measured object. Calibration is about scanner observing a special plate being put in various positions, so that the system can set the angle between the cameras, that could have changed with the influence of temperature and shocks.
Due to the type of the projection unit, there are two main scanner types:
- Structural light scanners
- Laser scanners
Modern structural light scanners mostly use LED projector and two cameras, which are tracking variation of displayed lines. This type of a system requires tripod or a robot on which the head would be mounted. Such a measurement takes place with in a static way. It means, that during a single scan neither the head nor the scanned object cannot move.
Laser scanners use a laser emitter which purpose is to light stipes on the measured object, whereas two cameras are registering their deformations. The process of measurement is carried out in a dynamic way, which means that the system is generating data in a constant way, without any interruption of singular scans, as it would be in structural light scanners. Thanks to that, the “tripod” a human holding the scanner that significantly increases the measurement and mobility features.
Honda Assist-e
Or in other words, a system that is capable of self-leveling and driving a motorcycle. After a few years since this concept has been introduced, Honda decided to step up their game and introduce a revolutionary system that is capable of doing such stuff, that even an experienced biker is not able to perform.
The system has been introduced first during Consumer Electronics expo in 2017, Las Vegas. It was fitted to an electric motorcycle, which was able to move on it’s own in low speeds. Not long ago, a second presentation of this project has been revealed and it’s easy to tell, that it made a big progress.
The solution is based on actuators that are placed in the rear part of the vehicle, mounted directly to the Axle-this is how the whole structure is being controlled. Frankly speaking, the whole mechanism is far from being compact, but it creates a feeling like it’s a ready to use production unit and would be ready to use with various Honda motorcycles.
Riding Assist-e is based on a system of sensors, that are controlling a gyroscope mechanism that is responsible to prevent the vehicle from tripping. On the presentation, we can see that the bike can stand and drive on it’s own.
Also, in the near future Honda is planning to reduce the risk of road accidents thanks to this system
Printing with sound. Sounds interesting?

3D printing is a method of applying a building material layer by layer and its selective bonding. Each technology uses a different material that is bonded in a different way. 3D printing can be divided according to the material used. There are three basic groups of 3D printing: thermoplastics in the form of a line, light-curable resins and powder technologies. But now thanks to Muthukumaran Packirisamy and Mohsen Habibi we can add one additional method to that list.
An alternative to the traditional solutions, using plastics and sometimes other substances, 3D printing techniques called direct sound printing (DSP), which uses ultrasound to create new objects, was created in the laboratory of the Canadian University of Concordia. A researcher’s work on this subject describes this method of using focused ultrasound waves to induce reactions in areas of small cavitation, which is essentially tiny bubbles. Extreme temperature and pressure changes lasting trillionths of a second can result in predesigned complex geometries that cannot be produced with known additive techniques.
“We found that if we use a certain type of ultrasound with a certain frequency and power, we can create very local, very focused chemically reactive regions,” Habibi says. “Basically, the bubbles can be used as reactors to drive chemical reactions to transform liquid resin into solids or semi-solids.”
Researchers experimented on a polymer used in 3D printing called polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). They used the transducer to generate an ultrasonic field that passes through the shell of construction material, solidifying the target liquid resin and depositing it on a platform or other previously solidified object. The transducer follows a programmed path, creating the desired product pixel by pixel. The microstructure parameters can be manipulated by adjusting the duration of the ultrasonic wave frequency and the viscosity of the material used. According to the authors of the technique, it is potentially an excellent alternative to the 3D printing technique in many applications.
References:
https://www.eurasiareview.com/01062022-direct-sound-printing-is-a-potential-game-changer-in-3d-printing/
One of the most powerful supercomputers will be in Poland
One of the most powerful supercomputers in the world will be installed in Krakow by the end of next year. The Academic Computer Center CYFRONET AGH has been selected by the European Joint Undertaking in the field of Large Scale Computing (EuroHPC JU) as one of 5 places in Europe where computers forming a pan-European data processing network will be installed, according to Cyfronet.pl:
“Poland is one of the 5 EU countries selected for the installation of a new generation supercomputing system – the machine will be delivered to ACK Cyfronet AGH”

The most powerful computer in the network will be JUPITER. It is the first exascale system in Europe – that is, it performs over 1018 floating point operations per second. It will be installed at the Jülich Supercomputing Center in Germany. The other four machines are DAEDALUS, which will be delivered to Greece, LEVENTE (Hungary), CASPIr (Ireland) and EHPCPL in Krakow.
Currently, Cyfronet has the most powerful supercomputer in Poland, Athena. The machine with the power of 5.05 PFlop is on the 105th position on the list of 500 most efficient supercomputers in the world and is one of the 5 Polish supercomputers listed there. It is known that the EHPCPL will be several times more efficient than Athena.
The goal of EuroHPC JU is to create one of the most powerful supercomputing infrastructures in the world in Europe. There are already LUMI (151.9 PFlop / s) machines in operation in Finland, MeluXina (10.52 PFlop / s) in Luxembourg, Karolina (6.75 PFlop / s) in the Czech Republic, Discoverer (4.52 PFlop / s) ) in Bulgaria and Vega (3.82 PFlop / s) in Slovenia. Also under construction are LEONARDO (Italy), Deucalion (Portugal) and MareNostrum 5 (Spain). The Finnish LUMI is the 3rd most powerful supercomputer in the world and the 3rd most energy efficient computer in the world. Poland Athena ranks high, 9th on the list of the most energy-efficient computers in the world.
“The selection of Poland as the place of installation of one of the EuroHPC JU systems is an important distinction, confirming the national competence in the field of maintenance and operational use of supercomputers at the world level.”
https://eurohpc-ju.europa.eu/eurohpc-joint-undertaking-announces-five-sites-host-new-world-class-supercomputers-2022-06-15_en
Processor powered by algae
Recently, scientists developed a processor powered by photosynthesis from algae. The creators of the small system are scientists from the University of Cambridge, and their processor has been working continuously for over a year. Their research gives hope for creating a stable, renewable power source for small devices.
The size of the entire system is comparable to the small AA batteries. It consists of algae, a small aluminum electrode and a microprocessor. Everything is made of cheap, widely available and mostly recyclable materials. The creators of the system say that it will be most useful in places where there is no access to energy networks, and where small amounts of energy are needed, like power sensors.
Our system does not have the problem of running out of energy because sunlight is used to produce it, he adds. During the experiment that is currently underway, algae are used to power the Arm Cortex M0 + processor. Powered by algae, the processor worked both indoors and outdoors. It was exposed to natural changes in light and temperature. We were impressed with the continuity of his work.
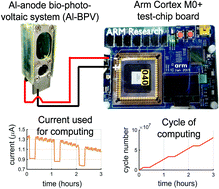
Algae do not need any special nutrition as they provide themselves and the processor with energy through photosynthesis. And although light is required to carry it out, the processor was powered even during periods of darkness. The algae were still carrying out metabolic processes.
The creators of the system point out that it would be impractical to power billions of the Internet of Things with currently used lithium-ion batteries. This would require more lithium than we currently produce. And traditional photovoltaic cells are manufactured with the use of environmentally hazardous materials. Hence the need to develop new, stable and environmentally friendly energy sources.
If you want to take a closer look at the solution, I recommend visiting the creators’ article: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2022/EE/D2EE00233G
Crypto winter not only for investors
We are witnessing another brutal decline and increasing losses in the cryptocurrency market. Bitcoin is breaking its ATH from the previous cycle from the top for the first time in history. A similar event has never happened before on Bitcoin.

The collapse on the cryptocurrency market affects not only the investors themselves. The cryptocurrency exchange Coinbase is slowing 18 percent of its workforce as cryptocurrencies have been in a retreat since last November. In recent days, however, the declines have intensified. Some cryptocurrencies started the week with drops by up to 20%. The most popular cryptocurrency – bitcoin – costs the least in a year and a half, reaching a rate below 20,000 dollars.
This crash is also influencing on cryptocurrency trading institutions. The New York cryptocurrency exchange Coinbase announced on Tuesday that it is firing 18% of their employees. Its CEO, Brian Armstrong, said in an open letter that the decision to lay off approximately 1,000 employees was “difficult” but was made to help the company survive the economic downturn.
Armstrong warned of a potential deepening of the cryptocurrency slump. “We seem to be entering a recession after more than 10 years of economic boom,” wrote Armstrong, adding, “The recession could lead to another cryptocurrency winter and could continue for a long time.”
Meanwhile, Coinbase shares have plunged around 80% this year. and 85 percent from IPO in April 2021. The company that used to be worth nearly $ 100 billion now has a capitalization of less than $ 12 billion.

