The Internet of Things
In today’s world, the term “Internet of Things” (IoT) has become an omnipresent concept. At its core, IoT is a network of physical objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, enabling the seamless collection and exchange of data. The core focus is on making our devices more intelligent and interconnected, establishing a world in which everyday objects can communicate and collaborate to boost their functionality and efficiency.
What IoT actually is?
IoT involves a system of interconnected computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, or objects that are provided with unique identifiers (UIDs) and the ability to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction. In simpler terms, IoT is the idea that everyday devices can connect to the internet and each other, enabling them to work smarter. From thermostats that adjust automatically to your preferred temperature to fridges that remind you to buy milk, IoT aims to make life more convenient.
A Brief History
The Internet of Things (IoT) originated in the early 1980s when a vending machine was connected to the Internet at Carnegie Mellon University. Coined in 1999, the term highlighted the potential of linking everyday objects online. By the early 2000s, technological advancements in wireless tech and miniaturized sensors accelerated IoT’s growth. This birthed smart home devices and expanded IoT’s reach across sectors like healthcare and manufacturing, shaping a future of seamless device communication and transformative impact.
Advantages of IoT
The integration of IoT brings advantages across various domains. One of the key benefits of this innovation is its ability to revolutionize convenience by automating processes and integrating devices, resulting in streamlined tasks. In the context of energy management, IoT plays a pivotal role in optimizing resource utilization, promoting sustainable practices and cost savings across industries like manufacturing. Another advantage is the improved surveillance and real-time monitoring, resulting in enhanced security measures and strengthened safety protocols. Businesses harness the interconnectivity of IoT to drive informed decisions, enhance operations, and deliver customized experiences, fuelling growth and creativity while boosting efficiency and competitiveness..
Disadvantages of IoT
However, IoT also brings some concerns. Privacy issues loom large as data generated by IoT devices becomes a potential target for breaches. Cyber vulnerabilities pose risks, raising debates about the balance between convenience and safeguarding sensitive information. Moreover, there is a growing concern about excessive dependence on technology, leading to conversations about the importance of human involvement and its consequences..
IoT in Smart Homes
The integration of IoT in smart homes ushers in a transformative paradigm. Picture a scenario where devices seamlessly interact—smart refrigerators not only manage groceries but also collaborate with online stores, autonomously placing orders as supplies diminish. This interconnectedness of IoT devices augurs unparalleled convenience, efficiency, and personalized experiences.
IoT in E-commerce
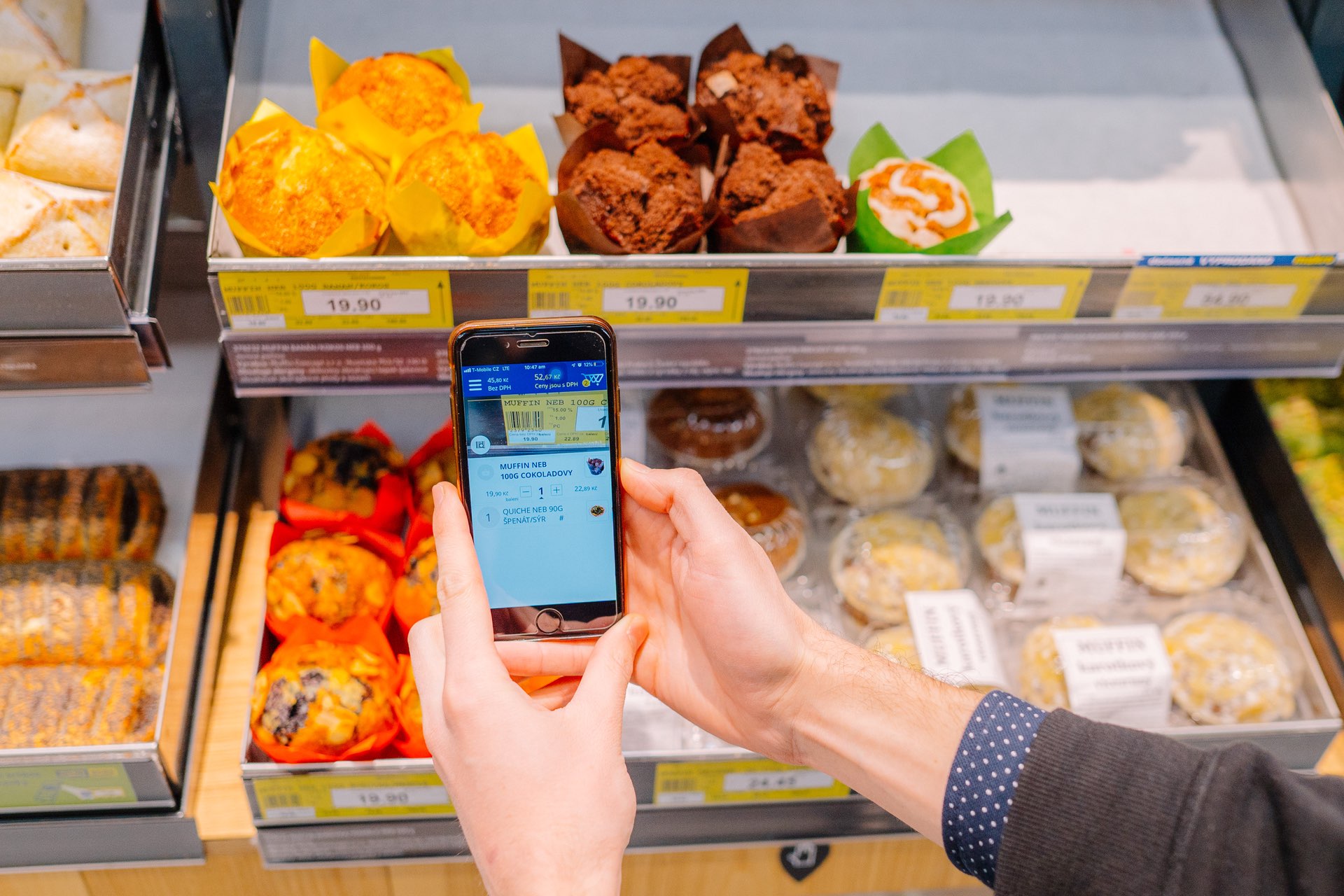
In the realm of e-commerce, IoT is reshaping business-consumer interactions. IoT-enabled devices detect low supplies and autonomously initiate orders. Retailers leverage real-time data for personalized recommendations, enhancing customer satisfaction. The integration of IoT simplifies transactions, offering consumers enhanced convenience and efficiency in their shopping experiences.
Conclusion
The discourse surrounding IoT often revolves around the balance between convenience and potential risks. While proponents emphasize the unparalleled ease and efficiency IoT brings, critics raise poignant concerns about privacy invasion and interconnected devices’ inherent vulnerabilities. Striking a balance between these viewpoints necessitates stringent regulations to mitigate risks while harnessing IoT’s potential. In addition, there is a pressing concern about the potential over-dependence on technology, giving rise to discussions about the essential role of human involvement and its effects. As these technologies continue to intertwine, ensuring data security and privacy becomes crucial, despite the promised convenience and efficiency. IoT’s progress reflects its diverse capabilities, demanding a mindful fusion of innovation and ethical factors to define this interconnected environment.
Sources:
- https://www.ibm.com/topics/internet-of-things
- https://www.oracle.com/pl/internet-of-things/what-is-iot/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_of_things
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-iot/
- https://www.javatpoint.com/iot-advantage-and-disadvantage
- https://unsplash.com/photos/turned-on-charcoal-google-home-mini-and-smartphone-anapPhJFRhM
AI generator used:
- Google Bard