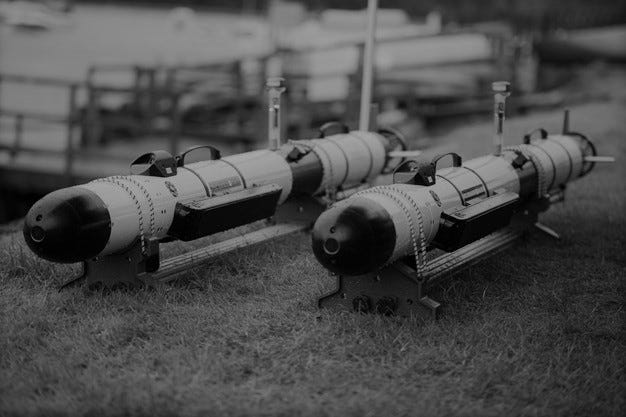
Our planet, Earth, is covered 70% by a large area of salt water which we call ocean. The total surface of all oceans in our planet are equal around 361 million kilometers per square.
Based on classification created by International Hydrographic Organization, we distinguish 5 oceans:
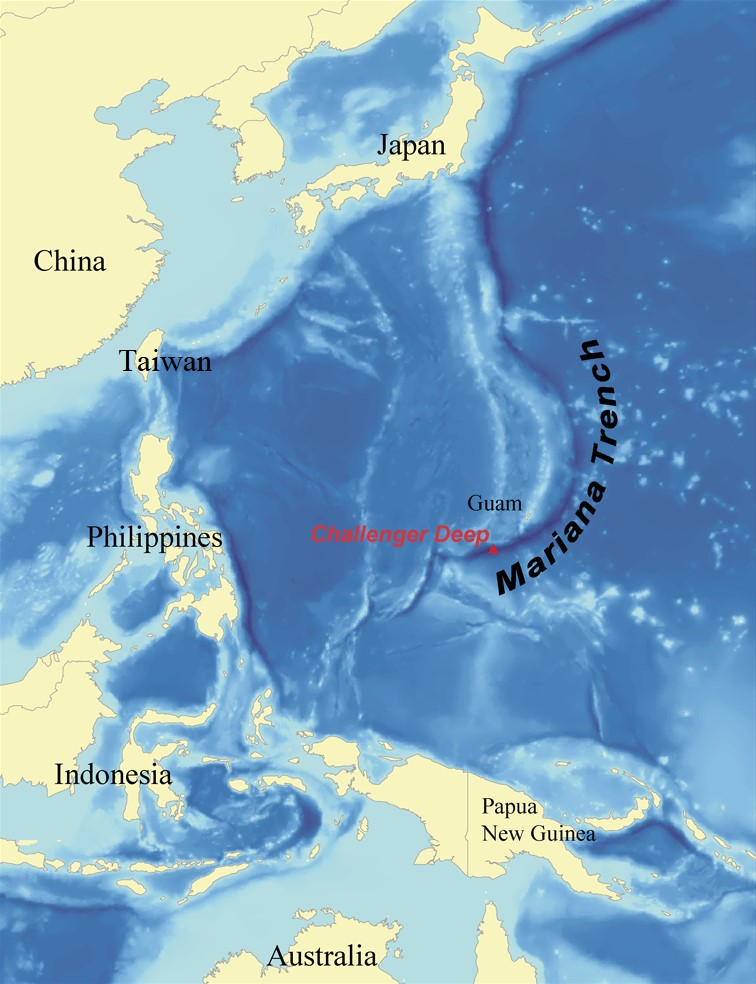
1. The Pacific Ocean – the biggest ocean which occupies around 30% of the whole Earth. Also, in the western part of the Pacific is located the Marian Trench that for now is known as the deepest place on our planet. The maximum measured depth is 10984 meters under sea level.
2. The Atlantic Ocean – the second ocean when it comes to surface in the world. This ocean covers 20% of our planet with the biggest trench equal 9219 meters under sea level.
3. The Indian Ocean – the third-largest ocean that covers 19,8% of the water on Earth’s surface. The deepest trench of this ocean is the Sunda Trench with a maximum depth of 7290 meters under sea level.
4. The South Ocean – the fourth-largest ocean placed in the south part of our planet. Its deepest part is South Sandwich Trench with the deepest point at level of 8266 under sea.
5. The Arctic Ocean – the smallest and shallowest ocean on Earth. It is situated around the Arctic. The deepest point of this ocean is the bottom of the region Amundsen around 4650 meters under the sea.
Oceans are badly big that people have discovered only a little part of them. Based on data less than 20% of the world’s ocean floor has been mapped in detail. Of course, humans are still working to create more information about the ocean floor but due to the hard conditions which are there it is a very slow process. However here with help comes AI that is bringing bright future to the exploration of the oceans because it will increase frequency of ocean expeditions and improve their efficiency. So, it is finally time for us to get more information about our planet?
1. Autonomous Seacraft.
First, AI can be used to automate submersibles that could work on their own. This action will give the opportunity to explore and map the seafloor for twenty-four hours per day. Without any doubt the area of exploration will grow immediately. Also, AI-powered submarines would decrease the risks of human lives from ocean expedition.
On the other hand, building such a vehicle is a risky project due to the condition that is in the deepest part of our oceans. Even the hardest elements which we know for today will not survive undamaged for long time on 8000 meters level under the sea level because of big pressure and corrosiveness of salt water. Unfortunately, today’s building material is going to be destroyed against ocean nature.
2. Ocean Data Analysis.
Using AI algorithms in oceans exploration can efficiently process and analyze large volumes of precise oceanographic data, including data from satellites, buoys, and underwater sensors. This capability allows for the rapid identification of patterns, anomalies, and trends in oceanographic variables such as temperature, salinity, and currents. Predicting the ocean’s condition will allow us to prepare properly for the ocean expedition.
However, relying too much on AI ocean analysis can be very misleading because data in the ocean is changing rapidly. Due to these algorithms can be inefficient and can generate wrong output.
3. Precision Mapping of Ocean Floor.
AI is revolutionizing the process of creating underwaters map thanks to advanced imaging technologies and machine learning algorithms. Sonars powered by this AI technology which are put under the water, are finding underwater resources, identifying potential hazards, and searching for helpful data that is really needed for ocean explorations. Moreover, such gear can measure the depth in unknown parts of oceans.
It is worth saying that very remote environments on large depth under the sea can cause errors in the process of mapping ocean data. Because of the lack of light, it is hard for AI to analyze data which is surrounding it.
4. Image and Video Analysis of Ocean.
AI-powered image recognition and computer vision can aid in the analysis of underwater imagery and videos. This is particularly useful for identifying marine species, studying underwater ecosystems, and monitoring the health of coral reefs. It is worth to add here that thanks to usage of image and video analysis we will be able to discover and describe new ocean species which have not been discovered before.
Although there are a lot of similar species in the ocean which cannot be correctly identified by AI. Hard conditions in the ocean have influence on bad quality of image and videos taken there. It would create errors or lack in the collected data which will extend the time of working with such ocean data.
Conclusion: AI is the new future of ocean explorations.
To sum up, AI is going to revolutionize ocean exploration. More ocean data will be gathered by it and new categories of submarines will be created. It will allow us to get more information and statistics from our oceans. Moreover, we are going to find new marine species and there is high probability that by using AI we will find new resources in the ocean that will give us power.
Disadvantages of using AI will be too much reliance on AI, data errors and of course costs which are produced by very hard and unpredictable ocean environment.
My opinion about this topic.
My thought about AI technology used in ocean exploration is that we must use it because we are standing in front of huge discovery of unknown places and species in our world. Nevertheless, we should remember that AI is not going to measure for us all mysterious about our water. We as humans need to use it in the correct way to get access to new data about the ocean.
I am looking forward to your comments about this interesting topic that without any doubt will bring us important facts and new information about our oceans.
Sources:
- https://pl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Strona_g%C5%82%C3%B3wna
Articles:
- https://www.aljazeera.com/features/2023/9/14/titan-implosion-is-ai-the-future-of-deep-sea-exploration
- https://annualreport.mbari.org/2022/story/unlocking-the-power-of-ai-for-ocean-exploration
AI Engine:
- https://deepai.org/chat