Computers have gone through big changes since their release to the public. They have gone from a cubed-shaped box to a simple folding laptop. They started heavy and ugly and through innovation became light and elegant. Their usage became much more simple and nowadays most of the population is using a computer. Each year new features are being added or updated to our devices and one of them could soon be “Typealike”.
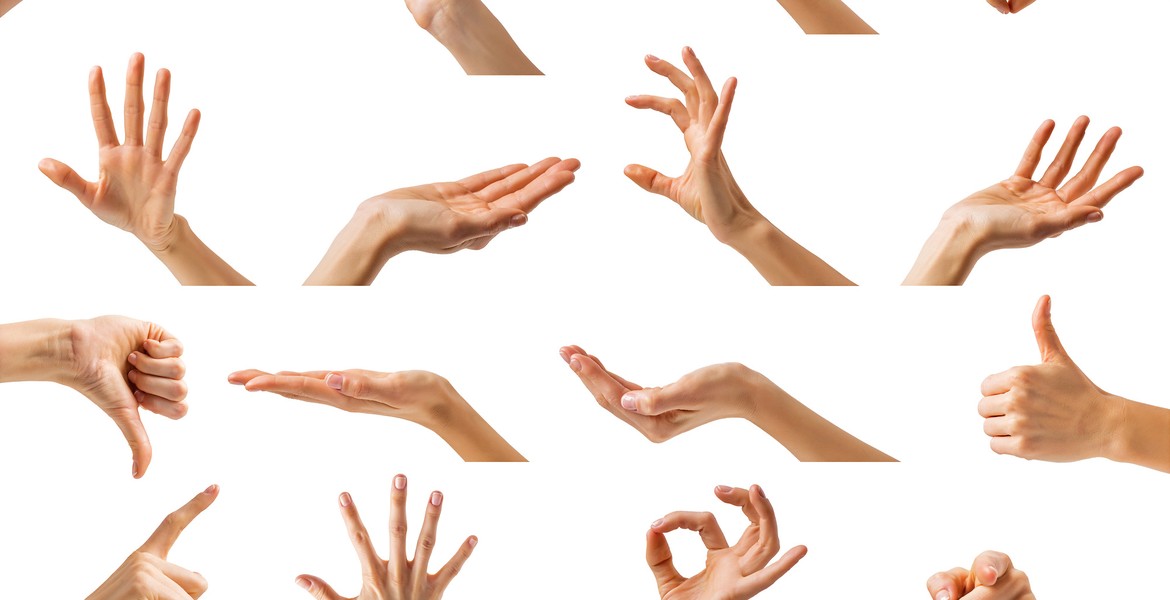
Typealike is a new technology that uses your computer camera to sense your hand movement and carry out commands based on what symbol you are showing with your hand. For example, when the user shows the webcam their thumb pointing upwards, the volume will change to higher. The technology was built by machine learning techniques and is able to understand a variety of different hand movements. Each user could set their own hand gestures to specific commands based on their liking. The point of this is to make the user experience faster and smoother.
The question is whether this system will actually make it easier to use the computer. You can change the volume of your device with a press of a button anyway so making a hand gesture to do it might not make such a big difference in accessibility. Perhaps Typalike could be implemented in different fields such as replacing the need for controllers for gaming consoles.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2022/01/220105094430.htm