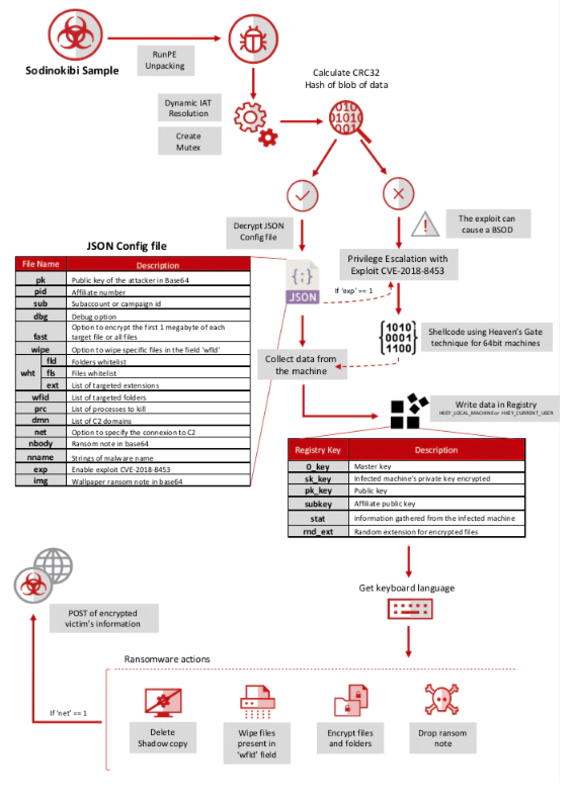
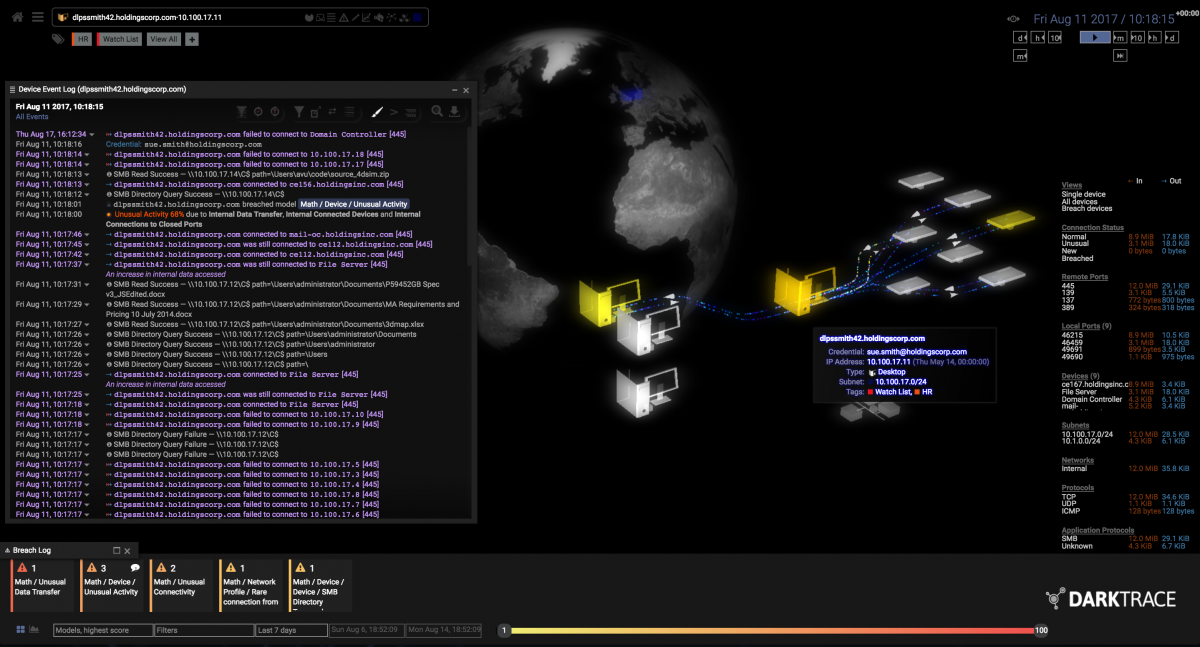
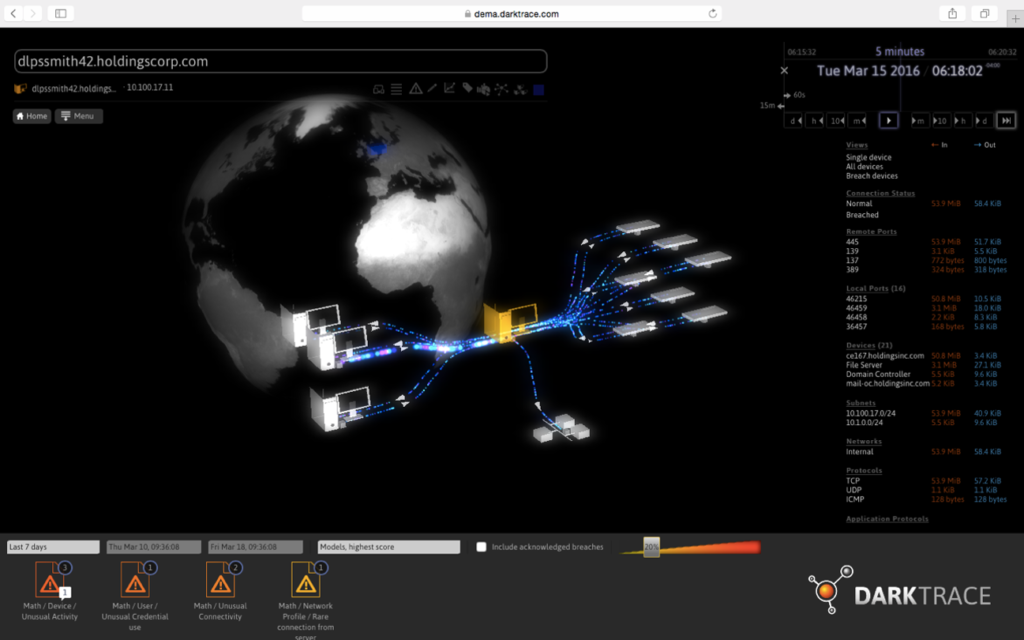
AI technology is developing unstoppable. In nowadays it’s important to have a high cybersecurity which will provide company’s data protection from being stolen by others. Businesses are facing an ever-expanding threat that endanger their data, operation, and financial well-being – ransomware attacks. The number of ransomware attacks increased as well in frequency and sophistication. They are targeting all kinds of companies on different fields trying to still valuable data. To navigate this evolving menace, it is essential that companies are understanding the dynamics of ransomware and have knowledge about improving their cybersecurity. It’s crucial to implement comprehensive strategies to defend against it.
The Ransomware Epidemic
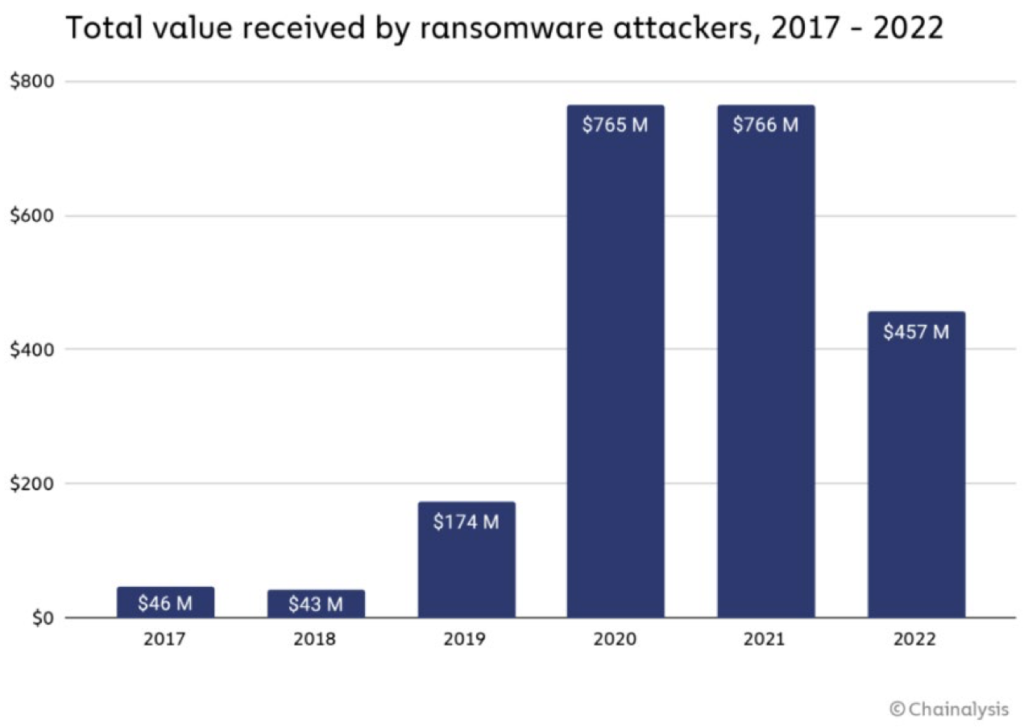
In recent years we can notice that ransomware attacks are happening often, becoming increasingly prevalent. Attackers are using sophisticated tactics to encrypt valuable company information and data, infiltrate systems.
Protecting Your Business
Companies should implement strict safety features because of the ransomed attacks that are a common thing in nowadays. Therefore, below I want to present some key strategies to consider:
- Regular backups: Do a regular and safe data backup at best on external drives. Later in case of a ransomware attack that clean, safe backup information can save your business from losing everything or paying huge money for getting data back.
- Multi-Layered Security: Invest in a comprehensive cybersecurity security, connecting firewalls, systems detecting attacks and control (IDC) to improve the company security.
- Incident Response Plan: Make sure that you have a clear incident response strategy which in case of an attack will specify what to do immediately. It might be for example isolating compromised systems or providing law enforcement. Good idea is to contact cybersecurity professionals’ contact information.
- Employee Training: It is important that all faculties are educated about the danger of phishing emails and other ways that valuable data might be stolen from us. Not being aware might link to vulnerabilities.
- Vendor and Supply Chain Assessment: Ensure that the supply chain in your company is fully secured and the suppliers are up to date. If there is a gap somewhere it means that somewhere might be weak spots that could be potentially exploited for example in ransomware attacks.
- Collaboration: Make sure you are up to date with the latest cyber and some trends. Find colleagues in different companies with whom you can collaborate and share information, so you can pass on important knowledge to each other to stay strong in your company’s cybersecurity through joint efforts.
Conclusion
Ransomware is a growing danger which every business should be aware of. It doesn’t matter how big the size or industry is because the attacks are the same for all of them. However, the greatest threat is human unawareness on this topic because the technology is developing constantly it is super hard to catch up with everything all the time. Artificial intelligence’s job is to try to find gaps in human ignorance causing making mistakes without awareness. We can’t fix it, so the only solution is to have in the company at least one high-improving cybersecurity. Usually, the cost of buying good prevention is still often significantly lower than in case we would have to recover data from a successful attack. Stay vigilant, stay secure, and protect your business from the ever-present ransomware threat.
Sources:
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/ransomware-growing-threat-businesses-brown-bsc-hons-msc-cissp
https://fintechmagazine.com/articles/how-fintechs-can-combat-the-growing-ransomware-threat
https://www.dni.gov/files/NCSC/documents/supplychain/Ransomware_Threats_and_Impact_to_Industry.pdf
Chat GPT
Images:
https://securityintelligence.com/articles/a-history-of-ransomware-and-the-cybersecurity-ecosystem/
https://www.dni.gov/files/NCSC/documents/supplychain/Ransomware_Threats_and_Impact_to_Industry.pdf