You’ve heard of LED lights, but OLEDs are set to revolutionize far more than just lighting. Inuru – founded on a mission to push OLED technology further. In flexible screens, sustainable manufacturing, and smart ads, Inuru’s innovations aim high. Propelling industries into the future, Inuru contends with challenges from scaling production to market competition. Yet the opportunities seem endless for these organic LED pioneers – let’s delve deeper into their futuristic visions.
Introducing Inuru: A Leader in OLED Technology
Inuru is a technology company founded in 2012 by Marcin Ratajczak with the goal of making organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays affordable and accessible. Through innovative manufacturing processes, Inuru has revolutionized the production of OLEDs, enabling the technology to spread into new applications and industries.
Inuru’s groundbreaking work with OLEDs has unlocked their potential in fields like consumer electronics, automotive, advertising, and healthcare. Their flexible OLED displays and lighting solutions provide energy-efficient and eco-friendly alternatives to traditional LED and LCD products. By simplifying OLED production, Inuru’s printing techniques have made the technology more budget-friendly and opened the door for creative new applications of OLEDs.

Inuru’s flexible OLED displays open up exciting possibilities for consumer tech and smart devices. Their bendable screens can wrap around curved surfaces, allowing for unique designs not possible with traditional LCD displays. Imagine smartphones with wraparound screens or smartwatches with displays that extend onto the band. Inuru is working to bring these futuristic concepts to reality. Inuru’s OLED technology is also more sustainable than existing options. Their simplified production methods require less energy and fewer resources, reducing environmental impact. OLEDs themselves are also eco-friendly, containing no toxic heavy metals. Additionally, OLEDs have a longer lifespan than LCDs, so displays require less frequent replacement.
The Future is Bright
Inuru has already begun revolutionizing industries with their affordable and innovative OLED solutions, but the future looks even brighter. As OLED technology continues to advance, costs decline, and new applications emerge, Inuru is poised to push the boundaries of possibility. However, they must continue optimizing production and reducing costs to overcome existing challenges, including high prices and limited scalability.
Still, with a keen eye for innovation and sustainability, Inuru has the potential to transform how we experience technology through the democratization of OLEDs. Flexible, affordable and eco-friendly, OLEDs could soon be lighting up our lives in ways we never imagined. The future is bright indeed with Inuru leading the way.
The Many Applications and Benefits of Inuru’s OLED Solutions
Inuru’s OLED technology has a wide range of practical uses that are revolutionizing industries and enhancing daily life. Their affordable, eco-friendly OLED products are being implemented in innovative ways across various sectors.
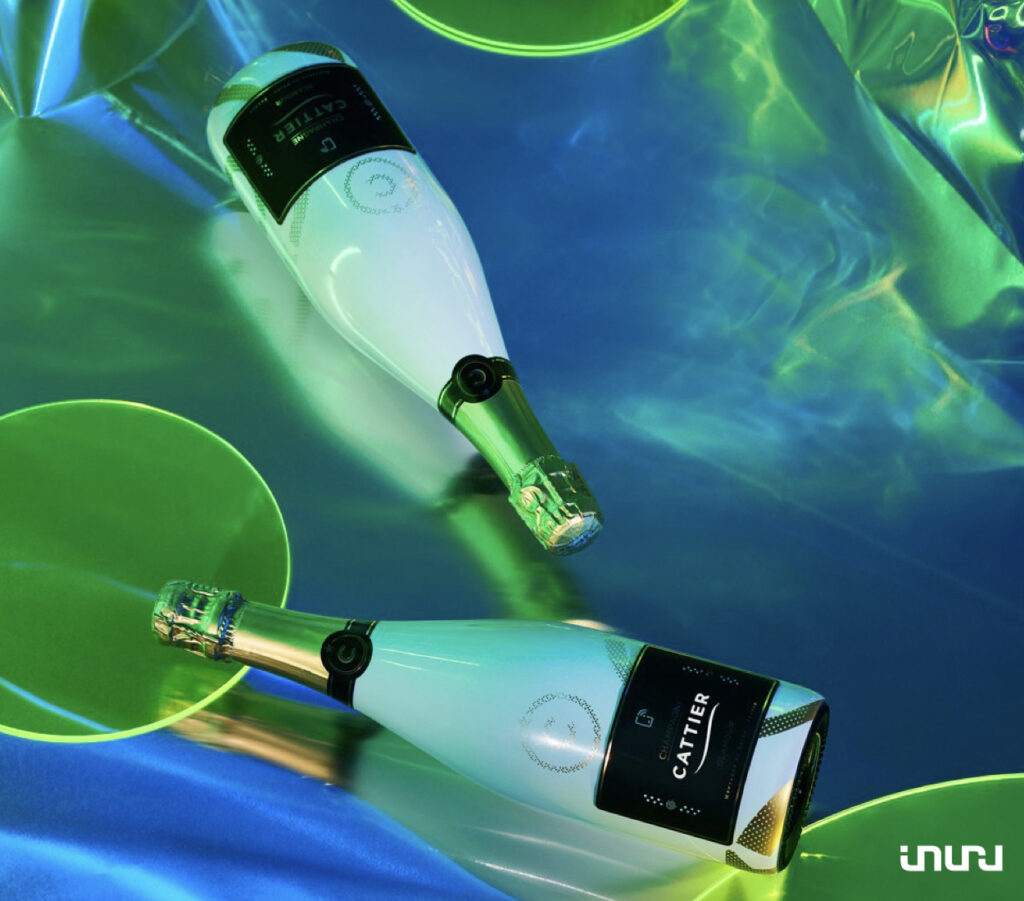
One of the most promising applications of Inuru’s OLED solutions is in the marketing and advertising space. Their flexible OLED displays and smart labels enable dynamic digital signage and product packaging that grabs attention. Brands can create eye-catching product designs and in-store displays that engage customers with animated content and interactive experiences.
Inuru’s mission to make OLED solutions affordable and accessible could significantly improve various facets of life and work. By collaborating with partners across industries like Coca-Cola or Displate, Inuru is discovering new applications for their sustainable, innovative technology that benefits both companies and consumers. Though still an emerging field, OLED technology promises to transform how we live, travel, advertise, decorate and stay informed in the years to come.
Conclusion
Inuru has established itself as a leader in OLED innovations and sustainable technology. By developing cutting-edge yet eco-friendly OLED solutions, Inuru is transforming industries and enriching lives.
OLEDs offer an exciting future of vivid visuals, immersive experiences, and energy efficiency. Inuru’s OLED displays and lighting are revolutionizing electronics, architecture, clothes, advertising, and more. Their flexible panels allow for curved screens and new form factors. Their lighting solutions provide natural-looking illumination that reduces energy usage.
As Inuru continues advancing OLED technology, the possibilities seem endless. However, scaling production and improving affordability remain challenges. Competition from major tech companies also threatens Inuru’s market share. Still, Inuru’s sustainable, human-centric mission could give them a competitive advantage.
You can see how Inuru is revolutionizing industries with their innovative OLED technology. From energy-efficient manufacturing processes to flexible displays and smart packaging, they are pushing boundaries and exploring new applications. While they face challenges scaling up and competing in the market, their sustainable vision and drive for innovation positions them well for the future. We will have to wait and see what other exciting developments come out of this promising Polish startup, but the possibilities seem endless. Wherever light is needed, Inuru may have a cutting-edge OLED solution.
Bibliography
- https://www.inuru.com/post/low-cost-oleds-for-low-cost-oled-labels-and-mass-market-adoption
- https://www.inuru.com/news/displate-and-inuru-announce-partnership-for-animated-luminous-posters
- https://siliconcanals.com/news/startups/inuru-raises-9-5m/
- https://www.inuru.com/post/what-it-takes-to-make-smart-packaging-become-reality
- https://www.inuru.com/news/cattier-uses-luminous-labels-for-champagne
- https://electronics360.globalspec.com/article/20330/oled-developer-inuru-illuminating-multiple-sectors-with-affordable-tech
- https://www.chip.pl/2022/08/wynalazek-ekran-oled-inuru-elon-musk
Written with the help of Hypotenuse AI.